Navigating Your Laptop's Interior: What Does the Hard Drive Look Like?
Introduction
Whether you are a tech enthusiast, a casual computer user, or perhaps aspiring to troubleshoot your laptop's issues yourself, understanding the internal components of a computer is essential. One of the significant parts worth knowing is the hard drive. Let's navigate the world of your laptop's storage system and identify the characteristics of a hard drive. In this article, we explore what a hard drive looks like from the outside, delve into its interior components, ways to identify it in your laptop, and offer you frequently asked questions concerning hard drives.
Why Is Understanding the Look of a Hard Drive Important?
Recognizing the physical appearance of a hard drive is not just about gaining familiarity with your laptop's inner workings. It carries more significant implications and potential advantages:
- Problem-Solving: Spotting the hard drive allows you to quickly assess, diagnose and if necessary, replace a malfunctioning drive.
- Optimal Performance: The make and nature of a hard drive can considerably affect your laptop's speed and operational efficiency.
- Informed Decisions: Knowledge of what a hard drive looks like equips you to make a prudent choice when purchasing a new drive or upgrading your current one.
In essence, understanding the aesthetics of a hard drive is a key step towards enhanced digital literacy, empowerment to self-repair, and achieving an optimal computing experience.
What Does a Laptop Hard Drive Look Like From the Outside?
Distinguishing the Exteriors of Traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
Visualizing the Evolution: Solid State Drives (SSDs)
The appearance of laptop hard drives might differ slightly, but understanding their standard look allows us to distinguish them easily. Worth noting, the two main variants of laptop hard drives are traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and the more modern Solid State Drives (SSDs).
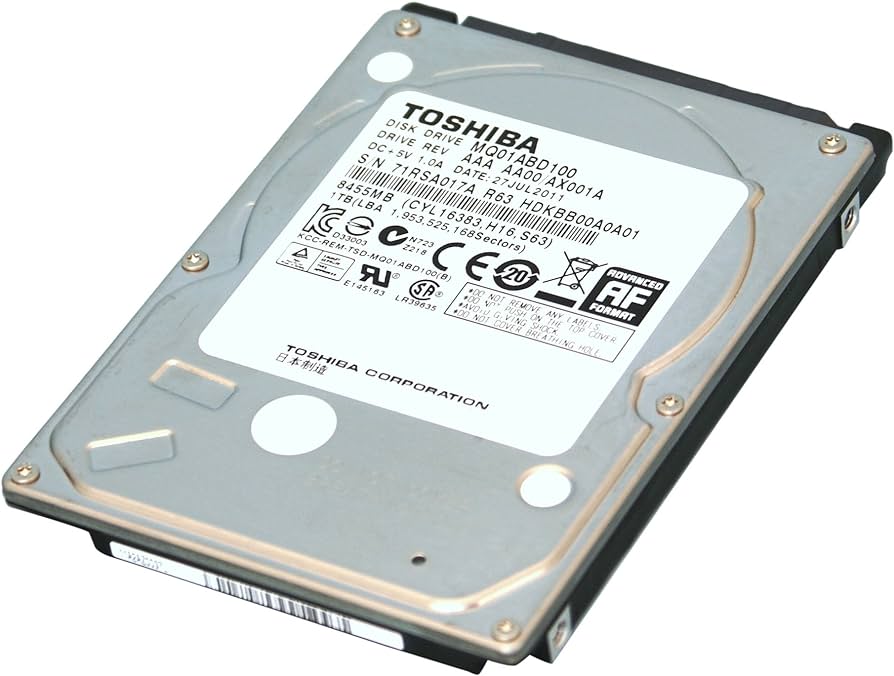
Outward Signature of Traditional HDDs
It's essential to remember that an HDD is typically rectangular and made of a hard, sturdy metal casing, slightly weighted due to the mechanical parts housed within. Following an industry standard, its dimensions are based on 'form factors.' Here's what to look for:
- Rectangular metallic body: A robust yet compact structure.
- Noticeably heavier: This is a result of the mechanical components it stores.
- Branded label: Usually the HDD carries a label on top detailing the manufacturer, storage capacity, and serial number.
- Connectors: Visible SATA connectors for both data and power supply.
Recognizing Modern SSDs
In contrast, SSDs are noticeable for their lack of mechanical parts, thus being significantly lighter and compact. They maintain a similar metal casing as HDDs, but thinner. More importantly, SSDs can feature different interfaces, indicated by the connector type.

- Metallic body: Similar to HDDs but thinner and lighter due to the absence of mechanical parts.
- Connector type: The type of connector, either SATA or NVMe, can help identify the type of SSD.
- Informatory label: Like the HDDs, these also have a label that lists essential details like manufacturer, storage capacity, and other relevant information.
By recognizing these physical characteristics, you can easily differentiate between an HDD and an SSD, enhancing your understanding of your laptop's components.
What Are the Inner Components of a Hard Drive?
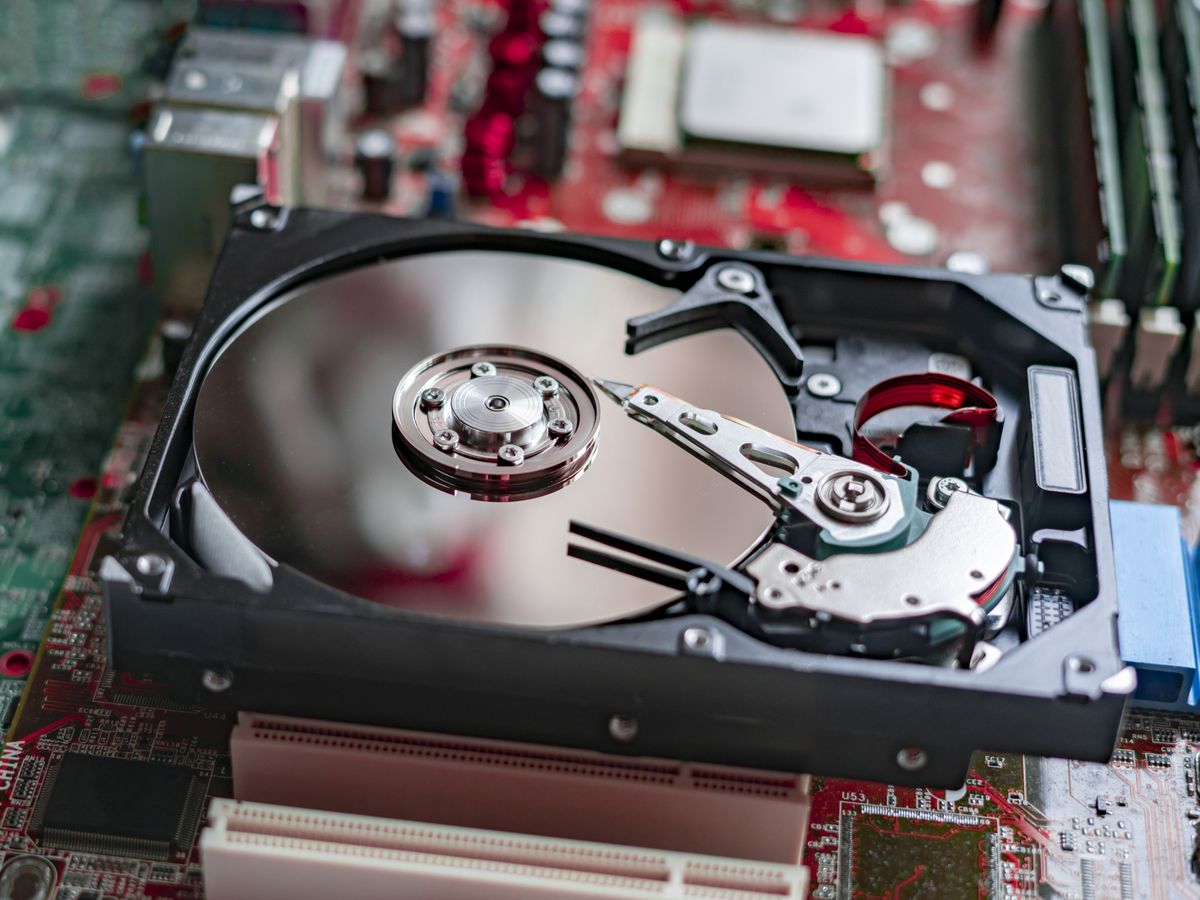
Inside A Conventional Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
Opening up a conventional HDD exposes you to a highly engineered arrangement of parts, displaying its characteristic mechanical operation. Here are the key components:
1. Platters: Resembling CDs stacked in a metal box, these are perfectly flat disks coated with magnetic material for data storage. Standard laptop HDDs use 2.5-inch platters.
2. Read/Write Head: It floats above the platter surface, moving around to read data from or write it to the platters using magnetic fields.
3. Spindle: This is what the platters rotate on – very fast. Standard laptop HDDs spin at 5400 RPM, while some run at 7200 RPM.
4. Actuator Arm: This moves the Read/Write Head across the platter surface.
These moving parts are why HDDs are thicker, heavier, more power-hungry, and possibly noisier and more vulnerable to damage from shocks.
Inside A Solid State Drive (SSD): A Different Perspective
An SSD, by contrast, has no moving parts. It's essentially a memory chip, encased to give it the same form factor as a laptop HDD, usually 2.5 inches, so it can slot into the same space. Some newer designs are more like RAM sticks (M.2 form factor) and go straight onto the motherboard. Here's what's inside an SSD:
1. Controller: This is the brain of the SSD. It directs data storage and retrieval, manages the interface with the laptop’s system, maintains the drive’s performance and more.
2. Flash Memory Chips: These store the actual data. They operate electronically, which is why SSDs work so much faster than HDDs — there are no moving parts to slow things down.
This absence of moving parts makes SSDs thinner, lighter, quieter, longer-lasting, faster, and more shock-resistant, but also more expensive. An SSD’s lifespan, however, can be quite long due to the absence of mechanical parts that could wear out.
How Can I Identify the Hard Drive in My Laptop?
Interested in finding out where the hard drive is located in your laptop? Being one of the critical components, the hard drive is generally designed to be fairly accessible for maintenance and upgrades. Here's a simplified guide on how to locate it in your machine:
1. Power Down and Disconnect: Safety is paramount. So, before opening the laptop, ensure it's turned off, unplugged, and the battery is removed if possible.
2. Flip and Locate Access Panel: Turn over your laptop to find a section usually secured with Phillips-head screws. This access panel generally leads to where the hard drive and other hardware components are housed.
3. Remove Access Panel: After confirming you have the appropriate screwdriver, cautiously remove the screws and lift the access panel.
4. Spotting the Hard Drive: In most laptops, you will find a rectangular metallic object—the HDD. If it's an SSD, it might look more like a large memory stick depending on the form factor.
Regarding the specifics, remember that the hard drive will often have a factory sticker with its make, model, and storage capacity information. Please note that hard drive location might vary depending on your laptop model, so consulting your laptop’s user manual could be invaluable.
Conclusion
As we dive into the hard drive's anatomy, it's crucial to distinguish between an HDD's and an SSD's innards as they considerably differ due to their unique technologies.
Related FAQs about what does the hard drive look like on a laptop
Why is it beneficial to know what my laptop's hard drive looks like?
Recognizing your laptop's hard drive can offer insights into your laptop's performance and capabilities. It can help diagnose and solve potential hardware issues. Additionally, when planning upgrades or replacements, an understanding of what your current hard drive looks like could be practical.
What are the main differences between an HDD and an SSD in appearance?
An HDD typically has a rectangular, sturdy metal casing and is slightly heavier due to internal mechanical components. Meanwhile, an SSD, lacking mechanical parts, is lighter and often thinner. The interface connectors also differ, with SATA being common for HDDs and both SATA and NVMe for SSDs.
Are certain laptop brands known to use specific types of hard drives?
Most laptop brands can utilize both HDDs and SSDs. The choice of hard drive depends more on the specific model and its targeted performance level. High-performance laptops and ultrabooks often favor SSDs due to their speed, while budget-friendly models might opt for HDDs.


