Unraveling the Mystery: Understanding the Internal Components of a Computer
Introduction
Computers are an inseparable part of our world, orchestrating a myriad of tasks ranging from simple calculations to complex simulations. But have you ever wondered what's beneath the sleek exterior of your device? This article aims to interpret the intricate language of computer hardware, breaking down the function of each internal component and answering some frequently asked questions. Whether you're a computer enthusiast or a newbie, this guide will enhance your understanding of how that machine on your desk works.
What Constitutes the Brain of a Computer? - The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
At the heart of every computer lies a component so fundamental that it's often likened to the human brain - the Central Processing Unit (CPU). It's the CPU that breathes life into our machines, interpreting and executing commands from the computer's software and hardware.
Let's delve deeper into the key attributes of a CPU:
- Cores: These are sub-units inside the CPU, responsible for executing instructions. Think of them as workers in a factory; in modern processors, you can find anywhere between two and 32 of them, each working simultaneously to manage different tasks.
- Clock Speed: Measured in gigahertz (GHz), this is the rate at which a CPU executes instructions. The higher the number, the faster the CPU can process data. For instance, a 3 GHz CPU can perform 3 billion instructions per second - quite the speed demon!
- Impact on Performance: The CPU profoundly affects the overall performance of a computer. A machine with a robust CPU can execute commands, run programs, and perform computations swifter, resulting in a smoother user experience.
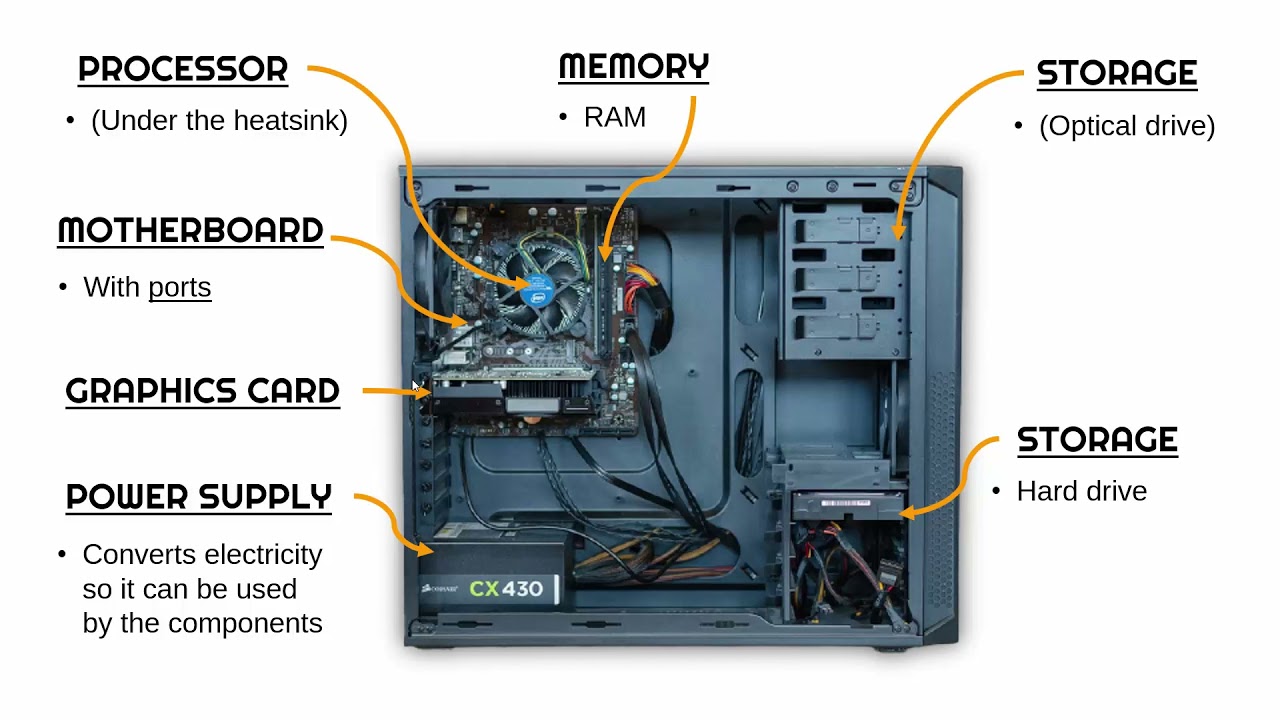
In essence, the CPU is integral to a computer's functioning, much like our brains are to us. How well your computer performs is intrinsically linked to the capabilities and characteristics of its CPU.
Why is the Motherboard Critical in a Computer?
Known as the nerve center of a PC, the motherboard serves as a crucial link, connecting all the computer's vital components and subsystems. It serves as the central hub where data gets traded and negotiated before being sent on their way. Here's a breakdown of its key responsibilities:
- Home to Vital Components: The motherboard houses essential parts including the CPU, memory (RAM), and expansion slots (PCI, PCIe). It physically hosts these parts and allows them to communicate effectively.
- Connector for Peripherals and Devices: The motherboard encompasses various ports that enable connection to input and output devices such as the mouse, keyboard, monitor, and speakers. These ports could include USB, HDMI, VGA, and more.
- Circuit Communication: The motherboard paves the information superhighway that all data travels on within the computer. It helps coordinate and regulate exchanges between computer sections. It's dutifully serving as the city's traffic conductor, ensuring smooth and swift data flow.
- Impact on System Performance: Motherboard quality and features can impact a system's speed, capacity, and potential for upgrades. A good motherboard supports high-speed components, abundant RAM, multiple hard drives, and a powerful graphics card.
In essence, the motherboard is involved in almost every aspect of a computer's function. Like a city's infrastructure system, it allows for efficient, unified operation across different computer sections. As such, understanding its role is pivotal to anyone looking to delve deep into computer hardware.
How do Different Types of Memory Function in a Computer?
Memory in a computer system serves as a temporary repository to access and work with data quickly. Broadly speaking, memory can be categorized into four primary types:
1. Random Access Memory (RAM): This is the volatile memory that temporarily holds data for ongoing processes. More RAM equates to smoother multitasking and faster operation. However, its contents are lost once the computer is powered down.
2. Read-Only Memory (ROM): ROM is a non-volatile, read-only form of storage that contains start-up instructions required by the computer. It cannot be modified by the user, ensuring consistent base functionality for the device.
3. Cache Memory: This processor-specific memory speeds up the data access process. It stores frequently used program instructions, reducing the dependency on slower main memory.
4. Virtual Memory: Acting as an extension of the physical RAM, the virtual memory makes programs believe they have access to more memory than what's physically available. It's slower than physical RAM but provides the illusion of "more space".
The roles of these different types of memory essentially revolve around data storage and rapid data retrieval, with the ultimate goal of enhancing the overall performance of the computer. Alongside their primary function, each memory type also brings some unique advantages in specific computing scenarios.
What Role do Hard Drives Play in Data Storage?
In tech-speak, hard drives are the answer to where all data ‘goes to rest.’ This encompasses your personal files, applications, and the operating system vital to booting up the computer. They're pivotal as they're designed to store data even when power is switched off.
Hard drives come in two main types, each having unique characteristics:
1. Hard Disk Drives (HDD): These employ a magnetic coating on rotating disks (platters) to store data. They've been a staple in computers for quite some time. The pros and cons of HDDs are:
- Pros: High storage capacity, cost-effective
- Cons: Slower access speeds, subject to mechanical failure
2. Solid-State Drives (SSD): These store data on flash memory chips and are gaining popularity. The benefits and drawbacks of SSDs are:

- Pros: Faster access speeds, more durable and reliable
- Cons: Higher cost per gigabyte of storage
Ultimately, the capacity and speed of the hard drive dictate how much data can be stored and the rate at which files load. A high-capacity, fast hard drive provides seamless access and more room for storage, enhancing overall system performance.
How does the Graphics Processing Unit Enhance the User Experience?
What is the component that largely governs the visual spectacle you perceive on your computer screen? It's the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), also known as the video card. This particular component dramatically influences the visual scenarios you experience, whether during gaming or COVID-induced video calls. Let's break down how it carries out its critical role:
1. Image Rendering: The GPU is primarily in charge of generating images, animations, and videos. Its task is to transform data into visual content that is displayed on your monitor.
2. Acceleration of Mathematical Computations: It executes swift mathematical computations, which effectively unburdens the Central Processing Unit (CPU). This division of labor enables the CPU to focus on other crucial tasks.
3. Enhancement of Graphics-Intensive Tasks: The GPU is the star player in situations that demand high-quality graphics. From gaming and 3D rendering to video editing, these tasks necessitate a potent GPU.
4. Improvement of Everyday Tasks: While the GPU is significant for heavy graphic tasks, its importance extends to simpler tasks like web browsing and video streaming, subtly improving the overall computing experience.
From cinema-like gaming experiences to efficient data processing, it's clear how the GPU significantly augments the user experience. So, next time you scroll through a website or play a visually-intensive game, appreciate the unseen efforts of the unsung hero - the GPU.
Why is the Power Supply Unit Essential for Computer Functionality?
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) is a crucial yet frequently overlooked component of a computer system. It performs the pivotal task of transforming raw power into a format that the computer's internal components can utilize. Here's why the PSU is indispensable:
- Energy Conversion: The primary function of a PSU is to convert the power from the mains into low-voltage electricity. This conversion is crucial as the computer parts require a steady stream of low-voltage power to function correctly.
- System Operation: Quite simply, without a PSU, your computer wouldn't turn on. All the major components, including the CPU, motherboard, and hard drive, rely on the power supplied by the PSU to work.
- Ensure Stability: A high-quality PSU is instrumental in preserving system stability. It accomplishes this by delivering precise power levels, thereby preventing harmful surges or lags.
- Component Longevity: By supplying clean and steady power, a good PSU can help prolong the lifespan of the computer's components, resulting in a more reliable and durable system overall.
In essence, the Power Supply Unit is the lifeblood of a computer, converting and regulating power for the seamless operation of all the computer's components. It is essential to invest in a good PSU to ensure optimal computer performance and longevity.
Conclusion
Understanding the internal components of a computer does not only empower you to comprehend how your device operates, but it also lays the foundation to troubleshoot issues, perform upgrades, and make informed purchase decisions. Every component has a critical role in the grand concert of computing, working harmoniously to deliver the performance that powers our digital world.
Related FAQs about what are the internal components of a computer
What is the difference between RAM and ROM?
RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read-Only Memory) serve different roles in a computer system. RAM is a volatile memory that temporarily stores data for ongoing processes, clearing as the computer shuts down. Conversely, ROM is a non-volatile, read-only storage that retains data even after power off, generally containing firmware or software that boots up the computer.
Is the CPU the most crucial component of a computer?
While the Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often termed as the 'brain' of a computer for its role in executing commands, all components are essential and work in tandem for a computer to function. However, the CPU does play a significant part in dictating the computer's overall performance.
How essential is the GPU for non-gaming tasks?
Even for non-gaming tasks, the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is crucial. It powers visual experiences like video calls and streaming, 3D rendering in professional applications, and even enhances browser performance. Thus, the GPU plays a significant role in improving everyday computing experiences.


