Unpacking the Core: Understanding the Main Components of a Computer Hardware System
Introduction
Navigating the intricate world of computer hardware systems may seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be. This article will deconstruct and provide an in-depth understanding of the primary components of a computer hardware system, their functions, and how they interact.
What is a Computer Hardware System?
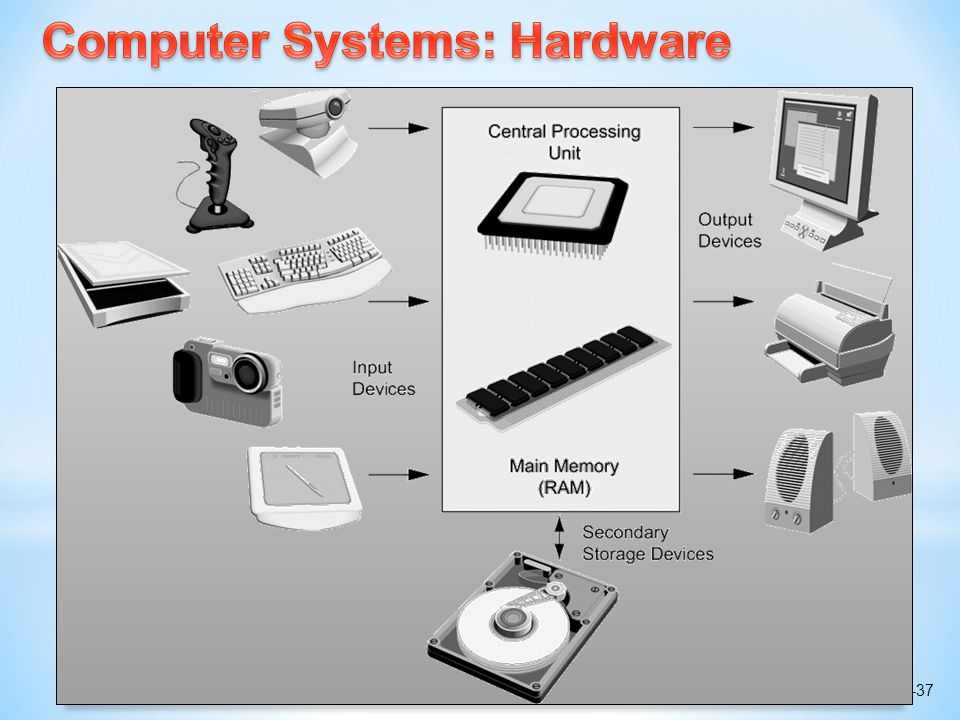
A computer hardware system entails the tangible, physical parts assembled to form a fully operational computer. These crucial components execute various tasks, process and store data, and generate output. Let's dissect a computer hardware system into its principal components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Termed as the 'brain' of a computer, the CPU carries out vital functions of executing program instructions. Each guided move you make on your computer from surfing the internet to using a spreadsheet, relies on the CPU's performance.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM works as the 'desk space' for your computer, storing data temporarily for quick access and processing. The RAM's size significantly impacts your computer's efficiency to handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Hard Drives: These are the computer's long-term memory units, storing data permanently even when the computer is off. The hard drive's capacity determines the amount of data you can store, while its speed influences the quickness of data access.
- Motherboard: Often seen as the heart of a computer system, the motherboard connects and allows all other components to communicate. It houses the CPU, RAM, and provides ports for hard drives and peripherals, contributing to the computer system's performance and upgrade potential.
Each component has its unique role but operates in harmony to constitute a comprehensive computer hardware system.
Why is the Central Processing Unit (CPU) Referred as the Brain of the System?
The Central Processing Unit (CPU), in many ways analogous to the human brain, holds a pivotal role in the functioning of a computer hardware system. It 'thinks', 'decides', and 'executes', thus enabling everything you do on your computer. Here's a detailed look at what makes the CPU the 'brain' of the system:
- Processing Powerhouse: The CPU processes almost every instruction that comes from hardware and software. Whether it's for browsing the internet or running complex software, the CPU executes the instructions necessary for these functionalities.
- Key Role in Performance: The efficiency of your computer hardware system largely depends on the CPU's performance. High-end CPUs can process more instructions in less time, leading to faster and more efficient computer performance.
- Execution of Instructions: Whenever an operation is initiated, be it opening an application or saving a file, it's the CPU's job to understand and execute these instructions.
- Speed of Operations: The clock speed of a CPU, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines how many instructions it can handle per second. Therefore, a higher clock speed equates to a faster processing capability.
Remember, while a robust CPU enhances performance, your computer needs well-functioning components in all aspects – including RAM, hard drive, and motherboard - for smooth running and optimal output. Choosing the right CPU should be a key consideration when configuring or upgrading your computer hardware system.
What Role Does Memory Play in a Computer Hardware System - Understanding RAM?
Random Access Memory, often abbreviated as RAM, is an instrumental part of the computer hardware mechanism. Acting as the computer's 'desk,' RAM offers a temporary workspace for active data processing. Here, let's delve into the vital role of RAM and how it influences the computer's performance.

- Functionality of RAM: When you initiate an application, the data is displaced from the static storage (hard drive) to the volatile RAM. The CPU, in turn, fetches and assimilates this data —implying that RAM is quite essential for an efficient multitasking affair.
- More RAM Equals Better Performance: The capacity of RAM directly influences how many tasks a computer can perform simultaneously. The larger the RAM, the bigger the 'desk,’ hence, more tasks can be undertaken.
Key Factors to Consider:
- RAM Size: Your computer's efficiency heavily relies on the size of RAM installed. Larger RAM means more room for temporary data storage, which can dramatically boost performance especially when using intensive applications or running multiple programs concurrently.
- DDR Generation: DDR stands for 'Double Data Rate,' and it refers to the series or generation of RAM. Each generation comes with speed improvements and power efficiency. For instance, DDR4 provides faster speed but less power consumption than DDR3.
The role of RAM in a computer hardware system is indeed comprehensive and critical; it's like having a reliable and efficient sidekick that aids in performing daily computer tasks with ease. So, understanding RAM will provide a better perspective on optimizing your computer's performance.
Why Does Storage Matter - A Close-Up View of Hard Drives and their significance?
Understanding data storage's impact begins with recognizing the crucial role hard drives serve within a computer's architecture. These devices behave as the computer’s long-term memory system, capable of holding data even when the computer is switched off. They store all forms of data, spanning from operating systems and applications to personal files and documents.
Consider the following aspects related to hard drives and understand their importance in our daily computing needs:
- Data Capacity: The total data that a hard drive can store is its capacity. It can range from a few gigabytes (GB) in older models to several terabytes (TB) in modern units. The larger the capacity, the more data you can store, from high-resolution images and videos to intensive applications and their associated files.
- Data Transfer Speed: The speed at which a hard drive can read and write data significantly impacts system performance. Faster speeds mean quicker file transfers, shorter loading times, and a smoother overall user experience. Modern Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are much faster than traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), leading many users to favor them despite the higher cost.
- Long-Term Reliability: Regardless of their capacity or speed, hard drives play a vital role in securely storing your data over the long term. Data loss can pose serious problems, so ensuring your hard drive is reliable and backed up regularly is a key consideration.
Understood in these terms, a hard drive's impact extends far beyond just storage. It indeed constitutes an integral part of the computer system, influencing both its performance and day-to-day user experience.
How Does the Motherboard Tie Everything Together?
The motherboard is effectively the epicenter of the computer, binding all the other components and enabling them to intercommunicate. It acts much like the central nervous system in our bodies, connecting various parts, facilitating interaction, and managing the power supply.
Here's a breakdown of its primary functions and how it acts as glue, tying everything together:
- Housing Key Components: The two key components, the CPU and RAM, are physically mounted on the motherboard. It provides the base for these components, maintaining their secure placement and ensuring efficient operation.
- Offering Ports for Additional Hardware: Apart from the CPU and RAM, the motherboard provides integrated ports for peripherals and hard drives. This means your printer, keyboard, or external hard drive can communicate seamlessly with other computer parts through the motherboard.
- Controlling Power Distribution: The motherboard isn't just a physical connection platform; it also manages power allocation to various parts. Without it, the power supply wouldn't reach the CPU, RAM, or hard drives.
- Enabling Communication Between Components: If the CPU is the brain of a computer, the motherboard is the spinal cord. It allows data to move between the CPU, RAM, and hard drives, resulting in a smoothly functioning computer system.
- Influencing Performance and Upgradability: The design and capabilities of your motherboard determine the system's overall performance and future upgrade possibilities. A high-quality motherboard is essential for a high-performance computer.
Hence, understanding the motherboard's role is vital to comprehend how a computer hardware system works holistically. This often overlooked component plays an instrumental part in knitting the computer's operations together.
Concluding the Core Components of a Computer Hardware System – What Roles Do They Play Together?
While each main component of a computer hardware system has its role, they work together as one cohesive unit. The CPU processes, the RAM stores temporary data, the hard drive holds long-term data, and the motherboard connects and manages all operations. These integral components form a fully functional computer system that caters to various computing needs.
Related FAQs about what are the main components of a computer hardware system
What is the difference between RAM and hard drive?
RAM and hard drives serve different purposes in a computer. RAM is a type of volatile memory, meaning it temporarily stores data that are currently in use. When the computer is shut down, data in RAM are lost. On the other hand, hard drives, serve as long-term, non-volatile storage. They retain data even when the computer is switched off.
How does the CPU interact with other components in a hardware system?
The CPU interacts with other components through a system bus on the motherboard. It fetches instructions from RAM, processes them, and writes the results back to RAM. It also communicates with other peripherals and hardware devices, such as the hard drive, via the motherboard, which acts as a communication hub.
Why is the motherboard considered the backbone of a computer system?
The motherboard is considered the backbone of a computer system because it connects all other components, such as the CPU, RAM, and hard drives. It facilitates communication between these components and coordinates tasks. Additionally, the motherboard provides ports for hardware peripherals and manages power distribution among the system's elements.


