Establishing Connections: The Interplay Between the Cpu And Other Elements of a Computer System
Introduction
The core functioning of any computer system revolves around the Central Processing Unit (CPU). It is the brain of the computer, responsible for executing commands and processing data. But its efficiency relies heavily on its interplay with other elements like memory (RAM), graphics cards, hard drives, system buses, and especially the motherboard. This article presents a comprehensive view of the complex network of connections that allow your computer to operate smoothly and efficiently. Read on to peel back the layers of your computer's operation and understand what connects the CPU to other components within a computer.
What Lies at the Heart of a Computer? A Look At The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The Central Processing Unit, known as the CPU, is the critical pivot around which all technological functions of a computer revolve. Acting as the brain of the computer, the CPU shoulders the responsibility of executing commands and working its way through enormous data sets to deliver seamless user experiences.
Key factors that highlight the importance of a CPU:
- Task Execution: The CPU interprets and executes most commands from the computer's hardware and software, making it an integral component of any computing system.
- Speed: The performance speed of a computer is largely determined by the CPU. The faster the CPU can process data, the quicker the overall performance of the device.
- Interconnectivity: The CPU interacts with key components like the RAM, graphics cards, hard drives, and the motherboard. This collaboration ensures smooth and efficient operations.
- Dependency: The overall functionality of other computer components heavily relies on the CPU. A problem in the CPU can hinder the efficient operation of the entire computer system.
Understanding these factors equips us with an overview of the role that a CPU plays in shaping the digital space within our devices.
Unfolding the CPU's Interaction with Other Components
Connection Between the CPU and Memory (RAM)
The relationship between the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and the Random Access Memory (RAM) is one of mutual dependence:
- The CPU extracts data and instructions from the RAM for executing tasks.
- The quick access of data is fundamental, resulting in the performance speed of your system. The higher the RAM capacity, the larger the 'desk space' the CPU has to lay out and access information, subsequently boosting efficiency.
CPU and Graphics Cards Interplay
The association between the CPU and a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), prominently contained on a graphics card, is essential for visually intensive tasks:
- The CPU offloads 3D graphics rendering tasks to the GPU, allowing parallel processing of data.
- Persistent communication occurs between the CPU and GPU to make real-time adjustments in games or while editing high-definition video.
Link Between the CPU and Hard Drive
The Hard Drive, crucial for maintaining all data even when the computer is powered off, also interacts with the CPU:
- The CPU needs to access the data stored in the hard drive to perform varied tasks, from loading your operating system to editing a spreadsheet.
- This interplay is facilitated by system buses, transporting data to and from the CPU and hard drive.
Understanding these interactions is vital, as it allows a more profound comprehension of how our computer systems work and can also guide us when looking to upgrade our systems or when troubleshooting issues. Just as a well-coordinated team can achieve more than a group of individuals, so too can a computer system where every component works in harmony with the rest. Through these multilayered interactions, our computers manage to perform complex tasks with efficiency and speed.
The Role of System Buses in CPU Connections
System buses have a pivotal role in the smooth and efficient functioning of the Central Processing Unit (CPU). Let's examine two integral types: Data Buses and Address & Control buses, and their impact on CPU connectivity.
Data Buses and Their Modulation of CPU Communications
Data buses serve as the actual pathways that ferry data between the CPU and other parts of the computer such as memory, graphics cards, and hard drives. These buses determine the rate at which data moves to and from the CPU, directly impacting the speed of information processing.
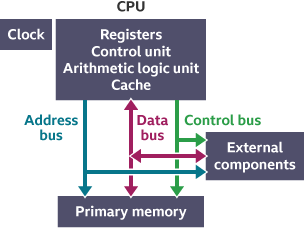
- A wider data bus can transport larger data volumes simultaneously, thereby significantly speeding up the CPU's operation.
- Conversely, a narrower data bus restricts data flow, slowing down the CPU's operations and potentially leading to a bottleneck.
Key Functions of Address and Control Buses in CPU Interactions
Alongside data buses, two other types of system buses come into play: Address and Control Buses.
- Address Bus: It acts as a navigation system, identifying the exact memory locations for data to be fetched or stored, facilitating the CPU's interaction with the memory. The width of the address bus influences how much memory the CPU can access.
- Control Bus: This bus functions as a traffic controller, directing the movement and operation of data traveling along the system bus. It oversees commands such as reading, writing, and interrupt requests.
In essence, system buses establish a critical framework for the CPU's efficient communication with other computer components. They regulate the flow, dictate the pace, and define the locations of data, ensuring optimal CPU performance.
The Importance of Motherboard in CPU Connections
The motherboard doesn't just function as a conduit for CPU connections - it's the very backbone that connects all the other components in a computer system. Let's delve into understanding how the motherboard serves as a facilitator for CPU connections and the various forms of interaction between it and the CPU.
Facilitating CPU Connections: The Data Highway
Think of the motherboard as a busy highway with lanes for data to commute. Here's how it assists CPU Connections:
- Data Traffic Control: CPU pins sit in the motherboard's sockets, creating a physical nexus for communication, essentially controlling the traffic of data between CPU and other components.
- Power Distribution: The motherboard distributes power from the power supply to the CPU and other components.
- Linking Memory and Storage: It connects the CPU with primary memory (RAM) and storage devices (hard drives), allowing data transmission between them.
- Expansion Slot Introduction: The existence of PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slots on the motherboards allows the connection of additional cards (videography, sound, etc.) enhancing the CPU's capabilities.
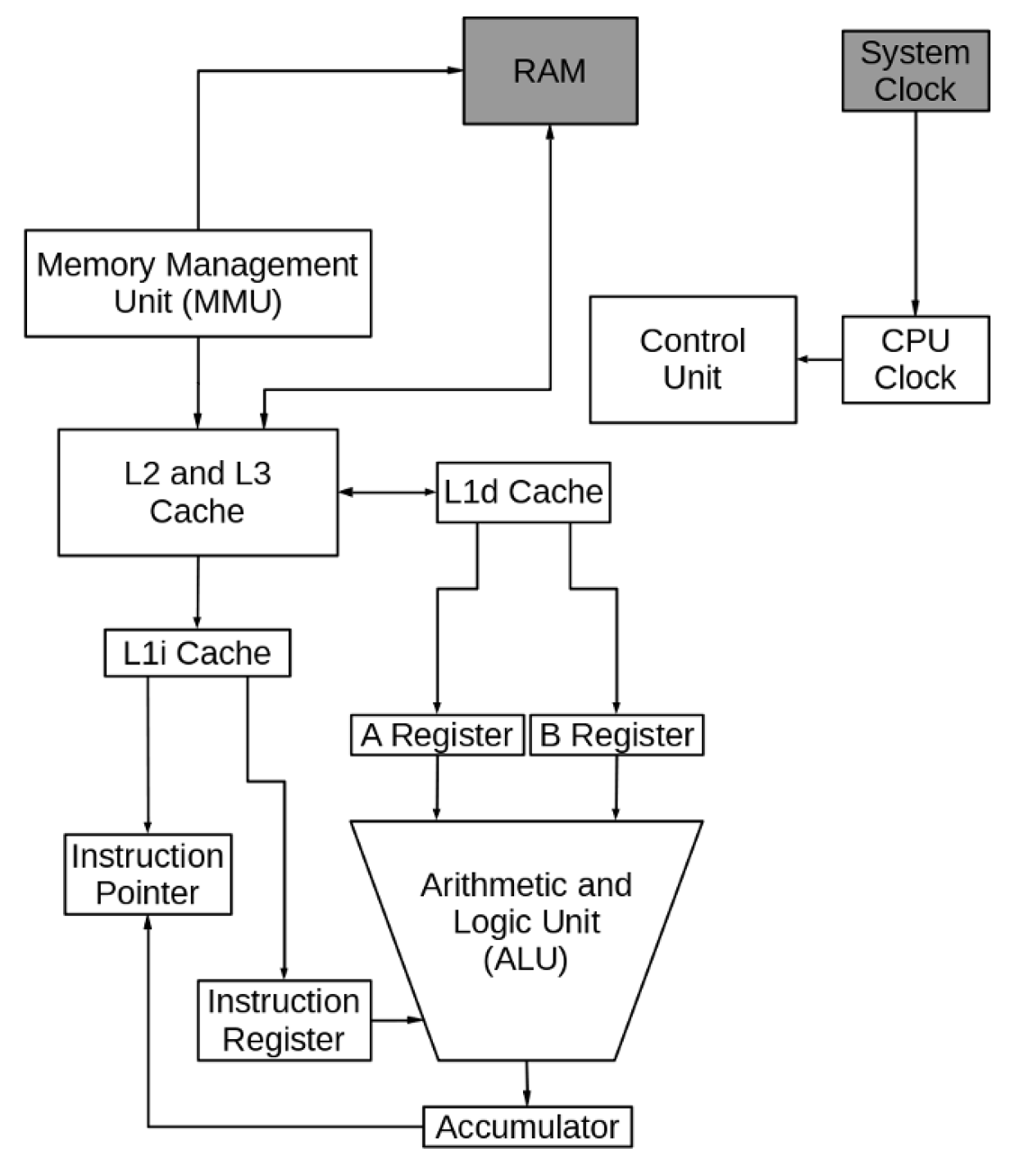
CPU-Motherboard Interactions: A Symbiotic Symphony
The communication between the CPU and the motherboard isn't one-dimensional. Let's unravel this symphony:
- BIOS Communication: The CPU interacts with the BIOS (Basic Input Output System) of the motherboard. It is the BIOS that initiates the process of a computer booting up, telling the CPU what to do.
- Power Management: The CPU, through the motherboard, communicates and controls when the system should enter the power-saving mode - ensuring energy efficiency.
- System Monitoring: The CPU engages with the motherboard’s system monitoring functions. This includes managing temperature, voltage, and fan speed controllers, allowing the CPU to throttle down in case of overheating, avoid voltage inconsistencies, and manage the cooling mechanism-all crucial for optimal CPU performance.
In synopsis, the capability and performance of a CPU highly depend upon its symbiotic relationship with the motherboard, making it a crucial element in delivering efficient computer performance. This mutual interaction simplifies the complex communication pathway between different computer components, ensuring a seamless user experience. By understanding how this connection functions, we can optimise our systems and troubleshoot effectively when needs arise.
Conclusion
The intricate interplay between the CPU and other components of a computer system is what makes our devices work so effectively. By understanding how the CPU, RAM, graphics cards, hard drives, system buses, and motherboard connect and interact, one can gain perspective on the complexity and engineering marvel that resides within our everyday computing devices. This knowledge also promotes effective troubleshooting and system optimization opportunities to deliver the best computer performance.
Related FAQs about what connects the cpu to other components within a computer
What is the role of the CPU in a computer?
The role of the Central Processing Unit (CPU) in a computer is to execute commands and process data. It’s the core component, often termed as the 'brain' of any computer system, responsible for performing most of the processing inside the computer.
How does the CPU interact with other components in a computer?
The CPU interacts with other components such as RAM, graphics cards, and hard drives through system buses. This interaction allows the CPU to access, process, and store data. The CPU also communicates with the motherboard to manage power distribution and system monitoring.
Why is the Motherboard important in CPU connections?
The motherboard is the main circuit board that interconnects other computer components with the CPU. It facilitates data communication between the CPU and other components, distributes power, allows expansion through PCI slots, and controls system monitoring through the BIOS.


