Demystifying Tech: What Are The Key Components Of A Computer System?
Introduction
This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of a computer system's key components. Aimed at deepening your understanding of what makes up your computer, this article will explore critical aspects such as the Central Processing Unit (CPU), Random Access Memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), inputn and output devices, and the integral role of the motherboard. Backed by simple explanations, you'll gain invaluable insights into how these components interact to provide you with the digital prowess your computer offers.
What Constitutes a Computer System?
A computer system is composed of crucial hardware elements that work together to carry out operations and processes. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Input Devices: These are the instruments through which we communicate with the computer. Examples include keyboards, mice, or touch screens.
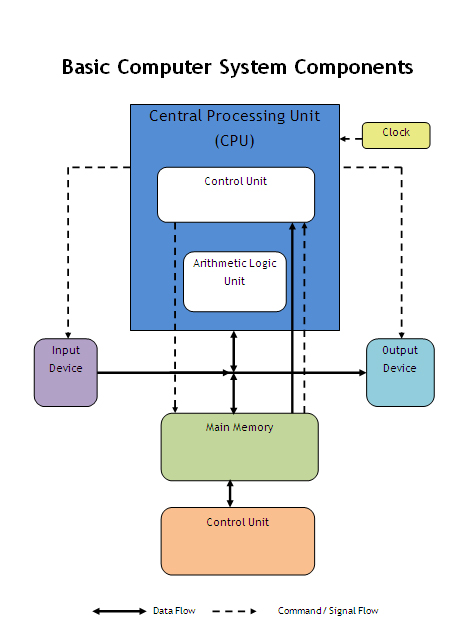
- Processing Unit: This is the heart of the computer where data is interpreted and processed. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the key component here.
- Storage Devices: These are the components used to store data, like hard drives or solid-state drives (SSD). They hold both temporary and long-term data.
- Output Devices: These are the tools that provide processed data in a user-friendly format. Monitors, printers, and speakers are all examples of output devices.
- Power Supply: This component brings the entire system to life, powering all the hardware to function as desired.
Besides these, various internal elements work together to ensure your computer runs smoothly and efficiently.
What is the Central Processing Unit and Why is it Important?
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) plays a pivotal role in a computer system as its brain, giving life to your interaction with the digital world. But what makes it so crucial? Let's delve into its key functions and comprehend its indispensability.
The Role of the CPU
* Data Handling: The CPU is the powerhouse of the computer system - it manages and interprets most commands from the system’s hardware and software, processing millions of instructions every second.
* Memory Management: The CPU oversees all primary and secondary memories, ensuring the correct data is accessible for each process.
* Distributing Tasks: Being the control center, the CPU allocates tasks to other hardware components, enhancing overall system efficiency.
Breaking Down the CPU
An efficient CPU comprises two pivotal parts:
* Control Unit (CU): This is the coordination hub within the system. The CU controls and directs all activities to ensure seamless operation.
* Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Specializing in mathematical and logical operations, the ALU performs computations necessary for various tasks.
With a top-notch CPU, a computer transforms into an efficient system capable of executing complex tasks seamlessly.
Why is the CPU Crucial?
Understanding the role of the CPU brings us to comprehend its importance. Simply put, a CPU is indispensable.
* System Operations: Without a CPU, a computer would just be a collection of hardware. The CPU breathes life into a computer, allowing it to execute tasks, run software, and facilitate user interaction.
* System Performance: A high-performing CPU translates to a fast, efficient computer system. The CPU's speed and efficiency mostly determine a computer's performance.
To sum it up, the Central Processing Unit is akin to the human brain. It controls, manages, and aids the coordination of all computer system functions, thereby making it the most essential part of a computer system.
Can You Tell the Difference between RAM and ROM?
RAM and ROM are prominent components of a computer's memory system, each serving distinctive roles and functionalities. This section will shed light on their individual characteristics, distinguishing one from the other.
● RAM - Random Access Memory
- *Definition*: RAM is a type of volatile memory that acts as a temporary storage space for data accessed by the computer in real-time, such as the running of programs or applications.
- *Volatility*: RAM is volatile, meaning it loses its stored data when the computer is powered off.
- *Functionality*: RAM offers space for the computer system to process and execute tasks. It acts like a workspace, providing the CPU with instant access to the data it needs to perform its operations.
● ROM - Read-Only Memory
- *Definition*: ROM is non-volatile memory that permanently stores crucial information needed for the computer system to boot up and operate. This information, also known as firmware, cannot be modified or erased.
- *Volatility*: ROM is non-volatile, implying that its stored data remains intact even when the computer is switched off.
- *Functionality*: ROM stores vital firmware, including BIOS instructions that guide the computer during startup. It initializes hardware and loads the operating system into RAM.
In essence, while RAM provides the computer system with a temporary workspace for dynamic processing, ROM serves as a durable storage vessel for indispensable firmware. RAM and ROM together contribute to the effective and efficient functioning of the computer system.
How Do Input and Output Devices Connect You to the Digital World?
Input and output devices act as essential conduits between users and the computer system, effectively connecting us to the digital world. Understanding their functionality can provide insights into their role in system operations.
Input Devices - Your Digital Communicators
Input devices are tools used to feed commands or instructions into the computer system. These devices assist in translating user actions or raw data into a computer-readable language. Common input devices include:
- Keyboards: Allows users to type in commands and data.
- Mouse: Provides point-and-click functionality for selections and commands.
- Scanners: Translates physical documents and images into digital format.
- Touch Screens: Allows users to interact directly with the computer display.
Output Devices - Delivering the Computer's Response
On the flip side, output devices present the feedback or result from the computer system in a user-understandable format. This conversion ensures that digital information processed by the computer is delivered as visuals, printed forms, or sounds. Frequently used output devices include:
- Monitors: help to visually display the output from the computer.
- Printers: Offers a physical, printed output of digital documents.
- Speakers: Provides auditory feedback or output from the computer system.
Key Takeaway
Input and output devices are essentially the bridge between humans and the computer's digital realm. While input devices facilitate interaction with the computer, output devices render the computer’s responses in a relatable and perceivable manner, thus enabling a seamless human-computer interaction.
How Does the Motherboard Act as the Computer's Central Hub?
Often referred to as the 'backbone' of a computer, the motherboard plays a relentlessly important role. It operates as the synthetic nervous system of any computer, interlinking all of its components while enabling them to communicate and interact efficiently.
Key highlights of a motherboard's functions are:
- Central Platform: The motherboard provides a central hub for all internal computer constituents. Whether it's the Central Processing Unit (CPU), Random Access Memory (RAM), hard drives, or graphic and sound cards, all need the motherboard for integration and functioning.
- Expansion Capabilities: Equipped with multiple expansion slots, motherboards give you the freedom to customize your computer system as per your requirements. This could mean adding a high-powered Graphics Processing Unit for intense gaming or an advanced sound card for a better auditory experience.
- Determining System Performance: The performance of a computer significantly relies on the motherboard. The efficiency in the communication between components can speed up or slow down the system, thereby underscoring the motherboard’s pivotal role in system performance.
Though unseen and often undervalued, the motherboard is essential. It hosts and connects all major components of a computer, enabling the communication and interaction required for your computer to function. The elaborate networks and connections in a motherboard constitute the complex yet essential architecture of every computer system, making it the lifeline for any digital device.
Conclusion
Demystifying the key components of a computer system aids not only in understanding its operation but also in optimal usage, troubleshooting, and enhancement. From the intelligence of the CPU to the memory management via RAM and ROM, and the connectivity facilitated by the motherboard, each component has its role in maintaining system efficiency and smooth running. The devices that let us interact with this digital world cap it all off, making the computer system an influential tool in today's digital world.
Related FAQs about what are the key components of a computer system
What Role Does Power Supply Play in a Computer System?
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) plays a crucial role in a computer system as it converts the power from the electrical outlet into usable power for the many parts inside the computer. It supplies power to the CPU, motherboard, hard drives, and other peripherals, enabling all hardware to function correctly.
How Does Software Interact with the Computer Hardware?
Software interacts with hardware through a series of coded instructions – programs or software. These give commands to the hardware components, instructing them on what operations to perform. The operating system acts as an intermediary, managing interactions between software and hardware.
What are Some Common Problems Related to Computer Components?
Common problems can range from hardware failure, overheating, and corrupted memory to bad sectors in a hard drive, malfunctioning power supply, and component incompatibility. Regular maintenance, hardware checks, and proper use and storage can help prevent many of these issues.


