Core Elements of a Computer System: Components And Functionalities
Introduction
The computer system you use in your home, office or school is so much more than the physical device you interact with. Deep within its hard exterior are several key components that work in sync to provide you a seamless digital experience. Knowing these elements presents a better understanding of how your computer system operates and can assist in troubleshooting possible issues. In this article, we delve into the core elements of a computer system, their components, and functionalities.
What Comprises a Computer System?
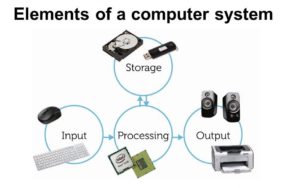
Inside the protective shell of your daily-use computer are some significant components that perform specific roles. Collectively, they form the sophisticated machine we refer to as a computer system. Understanding what these elements are and what they do provides a more comprehensive perspective of the system's operations. Here are four primary components that make a computer function:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Known as the computer's 'brain,' the CPU carries out most of the processing within the computer. It interprets and carries out instructions from the system's hardware and software.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): This component is a short-term data storage space that the system accesses for its current operations. RAM stores the data the CPU needs to process, enabling faster and more efficient performance.
- Data Storage Devices (HDD and SSD): HDD (Hard Disk Drives) and SSD (Solid State Drives) are the equivalent of long-term memory for your computer. These devices permanently store your files, images, videos, and the computer's operating system until you decide to delete them.
- Input and Output Devices: These are the peripherals you interact with daily, like the keyboard, mouse, monitor, and printer. They essentially serve as communication bridges between the user and the system.
Each of these components has a distinct role, and together they contribute to the computer’s overall performance and functionality.
What is the Role of the Central Processing Unit (CPU) in a Computer?
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) functions as the computer system's primary orchestrator for performing operations and executing instructions. Often hailed as the 'computer brain', it plays an instrumental role in dictating how efficiently your computer performs. If we were to liken a computer to an orchestra, the CPU would be the conductor, guiding each component to perform its function.
Below are the key functionalities of the CPU:
- Instruction Execution: The CPU's fundamental role is to process the instructions from both hardware and software sources. It reads code containing instructions about what operations to perform.
- Performing Operations: Various operations like arithmetic, logic, control, and input/output (I/O) operations are carried out in the CPU.
- Speed and Efficiency: These can be largely attributed to the CPU's performance. Its clock speed, which typically ranges in gigahertz (GHz), defines how quickly it can execute instructions. A CPU with a higher clock speed generally offers better performance.
To put its importance into perspective, a computer with a 3 GHz CPU performs roughly 3 billion instructions per second.
While the CPU is an integral part of achieving a seamless and efficient digital experience, other computer components also play their parts. Just as an orchestra performs best when all musicians work together, a computer functions at its optimal level when all components cooperate. However, the CPU undoubtedly remains the lead performer, playing the central role in making all operations possible.
How Does RAM (Random Access Memory) Function in a Computer System?
The RAM, an integral part of computer systems, performs a crucial role in determining the efficiency of processing tasks. Unlike other types of storage devices, RAM allows you to access any byte of memory instantaneously without the need to browse through previous bytes. Serving as the CPU's temporary data holding area, it enhances the speed and efficiency of the computer's performance. Nevertheless, the RAM's volatility results in the loss of information when the computer is turned off.
- Multitasking Efficiency: RAM's ability to temporarily store data from active applications allows computer systems to multitask seamlessly. A larger RAM size means a larger workspace for the CPU, enabling it to handle more tasks simultaneously.
- Speeding Up Operations: As RAM can be accessed much faster than other storage devices, it helps speed up the operation of the applications by ensuring rapid data availability to the CPU.
- Volatility: One characteristic that sets RAM apart is its volatility. Unlike the information held in storage drives, which are retained even when the system is powered down, the data in RAM is temporary. It gets wiped out every time the computer is shut off. This property is ideal for short-term data processing but unsuitable for long-term data storage.
Area of Improvement: While RAM significantly boosts system performance, constant advances in technology continually demand more RAM. Investing in higher RAM capacity can help computers keep pace with more advanced software and provide a smoother user experience.
In summary, the functionality of the RAM plays a vital part in your computer system's speed and efficiency. Each time you turn on your computer, the role of the RAM begins, speeding up operations, allowing multitasking, and assisting the CPU to ensure the smooth running of your system.
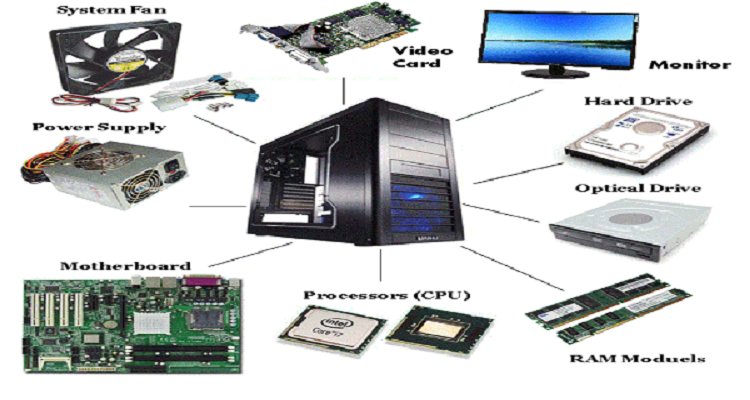
HDD and SSD: What Do These Storage Types Mean for Your Computer System?
When selecting a computer system, one crucial aspect to understand is the role of HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) and SSDs (Solid State Drives). These essential components perform the task of storing and keeping your data intact. They differ greatly in their construction, speed, durability, and cost.
- HDDs: These leverage mechanical parts to read and write data. While they are often more cost-effective, HDDs may lack the speed and robustness offered by SSDs. Key aspects of hard disk drives include:
1. Storage Capacity: They often provide higher storage capacity.
2. Cost-effectiveness: HDDs are generally cheaper than SSDs, especially at larger capacities.
3. Speed: The read/write speed of HDDs is typically slower compared to SSDs.
- SSDs: These devices utilize microchips to store data, significantly boosting speed and durability. However, they can be more pricey. Essential features include:
1. Speed: SSDs provide rapid boot-up times and faster application launch speed due to the absence of moving parts.
2. Durability: They are more robust and resistant to physical shock.
3. Cost: SSDs tend to be more expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs.
Understanding the difference between these two storage types assists users in choosing a storage drive based on individual needs and preferences.
How Do Input and Output Devices Facilitate Interaction with the Computer System?
Input and output devices are integral links in the communication chain between the user and the computer system. These devices, as much as the CPU or RAM, determine your interaction quality with your computer due to their direct role in information exchange. Below, explore their contributions to the computer's overall functionality in depth.
Understanding Input Devices
Input devices are indispensable elements designed to interact with the computer, providing it with the raw data to process. The input devices serve as the user's line of communication with the computer system. They include:
- Keyboard: Perhaps the most fundamental input device, the keyboard, allows users to enter text data and issue commands to the computer. It is an essential tool for programming and writing tasks.
- Mouse/Trackpad: These devices facilitate point-and-click navigation, making it easy to select and interact with on-screen options.
- Scanner: This device scans images or documents and converts them into digital data that the computer can process.
- Microphone: Useful for voice inputs, such as voice commands or voice chat.
- Webcam: This hardware captures video for various purposes such as video calls, recording, or facial recognition .
The Role of Output Devices
Output devices process output data from the computer, translating it into understandable information for the user. Here’s highlighting a few key ones:
- Monitor/Display: The primary output device, which creates a visual representation of processed data, enabling the user to view and interpret the result.
- Printer: Converts digital data into tangible documents or images, creating permanent physical copies.
- Speakers: Audio outputs form the computer are converted into sound waves that users can hear directly.
- Projector: This allows users to display digital images or videos on a larger scale, such as on a screen or wall.
Input and output devices modulate the engaging interaction between the user and the computer system. Through keyboarding commands to viewing on-screen results, they facilitate a comprehensive, dual-channel line of communication, thus optimizing the digital experience in its entirety.
Conclusion
Understanding the basic components of a computer system can help enhance your usage and troubleshooting skills. Each component, from the CPU to the RAM, to the various storage and input/output devices, serves a distinct purpose that contributes to the computer’s overall efficiency and functionality.
Related FAQs about what are the basic components of a computer system
What are the differences between RAM and storage in a computer system?
RAM and storage play distinct roles in a computer system. RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a form of volatile memory used for temporary data storage during system operations. It provides the CPU with quick access to the data it needs to execute tasks effectively. Storage, on the other hand, refers to non-volatile devices such as HDD (Hard Disk Drive) or SSD (Solid State Drive) which provide long-term storage for data such as files, applications, and the operating system.
How does the CPU affect the computer's performance?
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is often likened to the 'brain' of the computer. It processes instructions and performs the operations necessary for the functioning of the computer system. A powerful CPU can execute more instructions per second, which leads to improved overall performance. Factors such as clock speed, number of cores and threads significantly influence a CPU's effectiveness.
How do input and output devices impact user experience?
Input and output devices are instrumental in determining the user's interaction with the computer system. Input devices like keyboards and mice allow users to provide instructions to the system, while output devices such as monitors and speakers turn processed data into readily understandable information. These devices play a pivotal role in facilitating a smooth and effective human-computer interaction.


